Over 7 billion smartphones have been produced since 2007. These smartphones have changed the world in many positive ways, but the manufacturing of the phones has a devastating impact on our planet. Greenpeace states in a report that a new business model is needed in order to reduce the negative impact of smartphone production.
Main findings
According to Greenpeace, phones are being produced following a linear manufacturing model, based on a short-term profit driven perspective. Issues around resource extraction, exposure to chemicals in the manufacturing phase, energy consumption and a growing e-waste stream persist.
The main findings of the report are:
- “7.1 billion smartphones have been produced since 2007.
- More than 60 different elements are commonly used in the manufacturing of smartphones. While the amount of each element in a single device may seem small, the combined impacts of mining and processing these precious materials for 7 billion devices is significant.
- Since 2007, roughly 968 TWh has been used to manufacture smartphones, which is nearly the same as one year’s power supply for India (973 TWh in 2014).
- Only two (Fairphone and LG G5) of 13 models reviewed had easily replaceable batteries. This means consumers are forced to replace their whole devices when the battery life starts to dwindle.
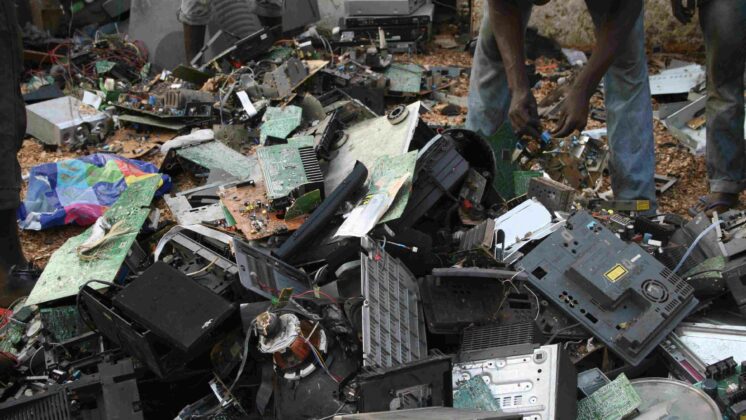
- In 2014 alone, e-waste from small IT products like smartphones was estimated to be 3 million metric tons. Less than an estimated 16 percent of global e-waste is recycled.
- At end-of-life, current design makes disassembly difficult, including the use of proprietary screws and glued in batteries; therefore, smartphones are often shredded and sent for smelting when “recycled.” Given the small amounts of a wide diversity of materials and substances in small devices, smelting is inefficient, or ineffective, at recovering many of the materials.”
Recommendations
Smartphones are designed in such a complex way that refurbishing or repairing a damaged phone becomes more and more difficult. Smartphone manufacturers should follow a new business model, where they take into account the impacts of the devices on our planet and by making them easily repairable.
Download the report ‘From Smart to Senseless: The Global Impact of Ten Years of Smartphones’